Heading Control on Differential Drive Wheeled Mobile Robot with Odometry for Tracking Problem
Abstract
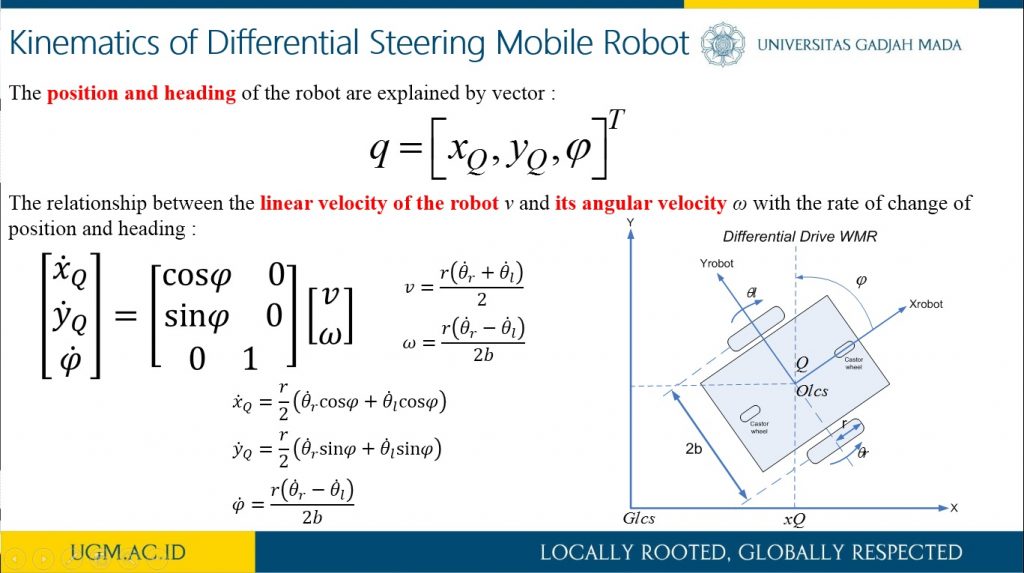
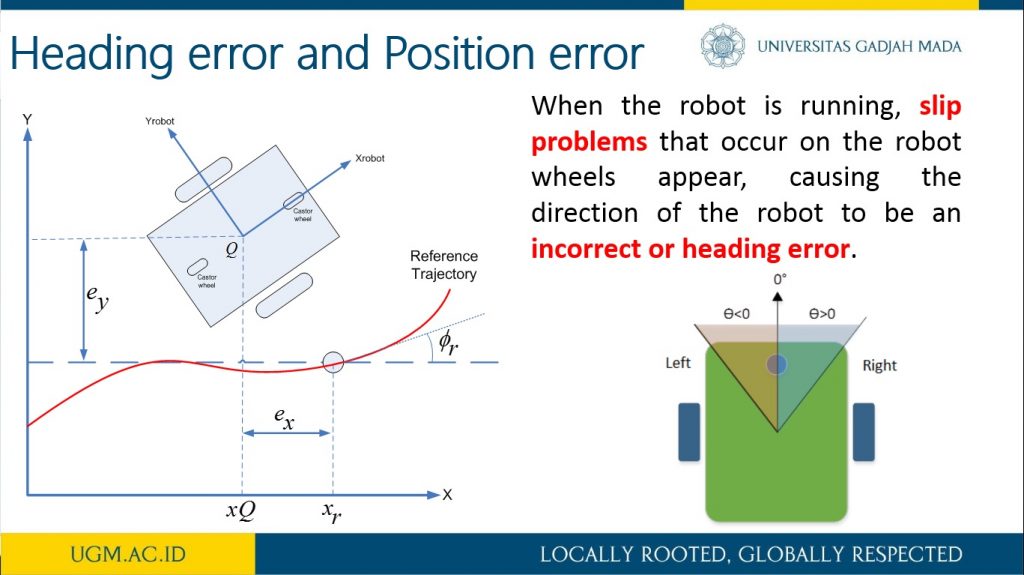
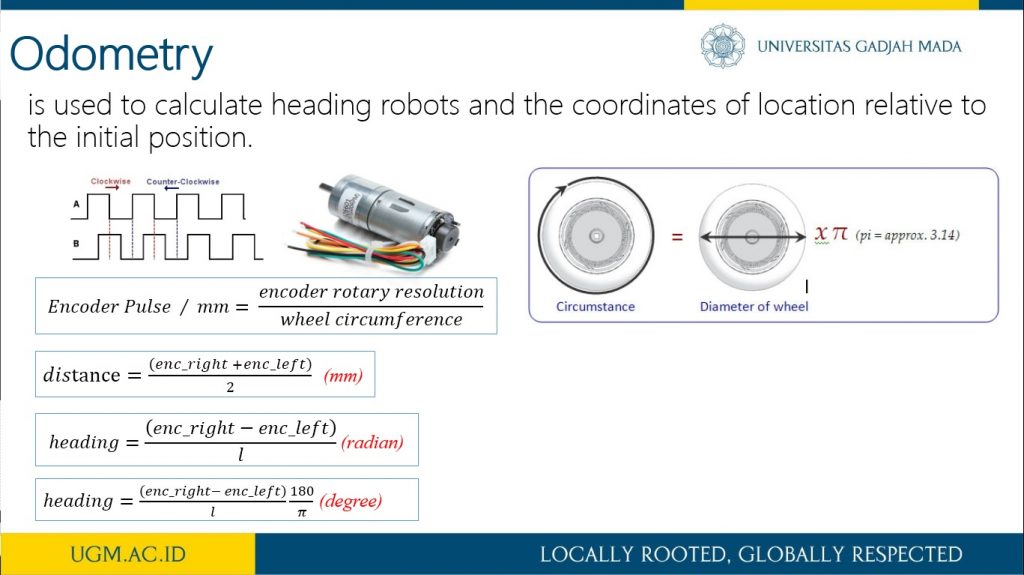
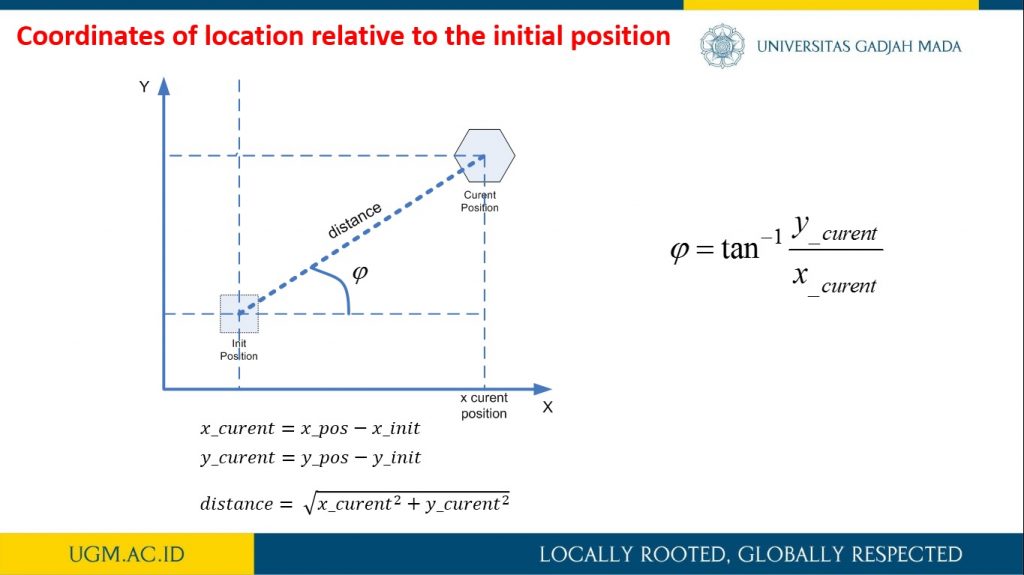
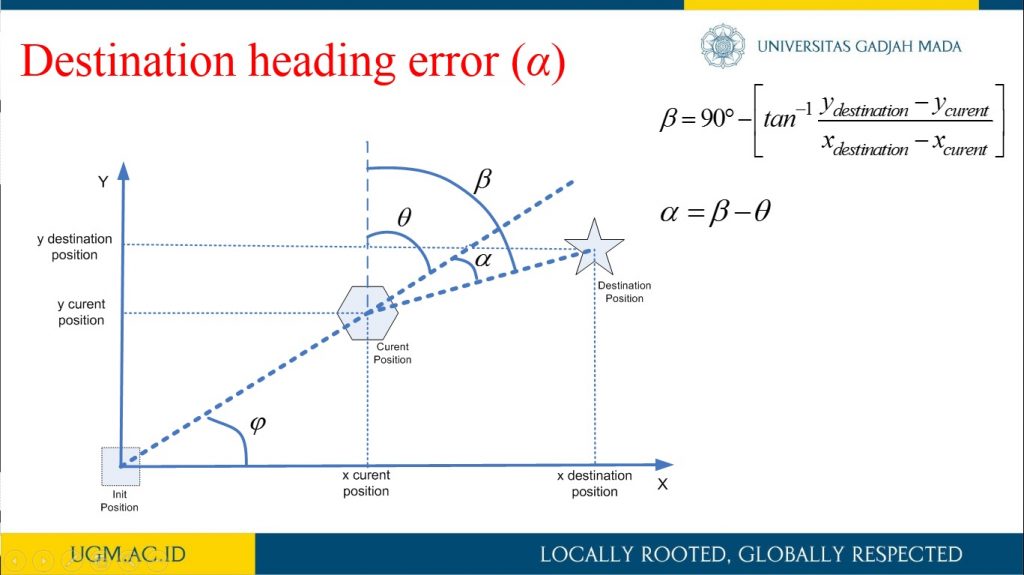
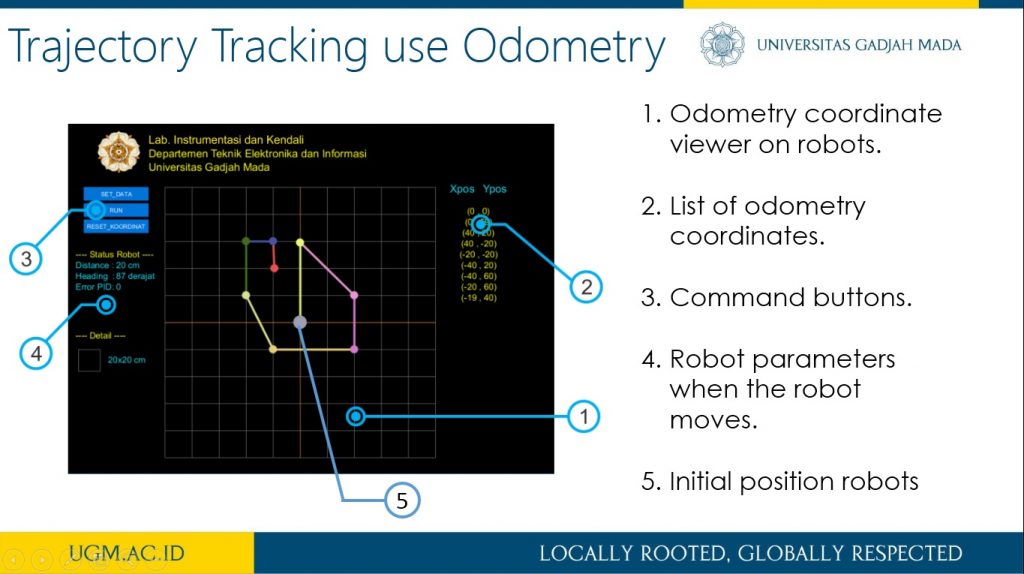
This research describes the process of designing odometry and heading controls from a differential steering wheeled mobile robot (DSWMR). The odometry system aims to estimate the position relative to the initial position of the robot to estimate changes in position from time to time in the trajectory tracking process. The problem that often arises in the tracking problem is the heading error that can be caused by a slip on the robot wheel or an irregularity between the speed of the DC motor on the robot wheel. Heading errors in DSWR can be obtained with the help of a rotary encoder located on a DC motor. This work applied PID control to obtain the heading error close to 0 degrees on the odometry system for trajectory tracking. It works by controlling the rotating speed of each DC motor on the robot wheel. The results of the PID control parameters implemented on the DSWMR were obtained from the results of tuning experiments with Kp = 3.0, Ki = 0.0003 and Kd = 2.5.

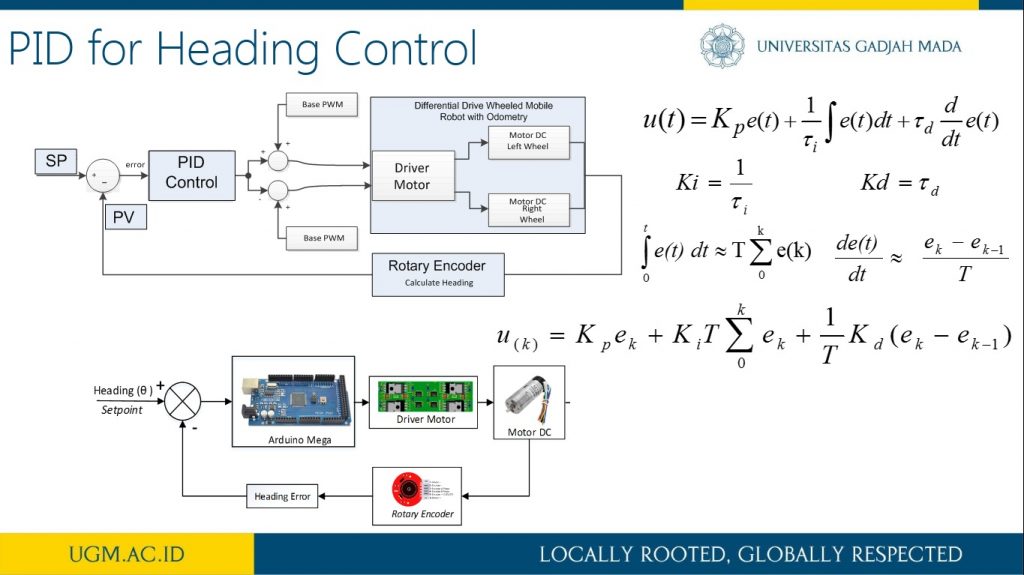
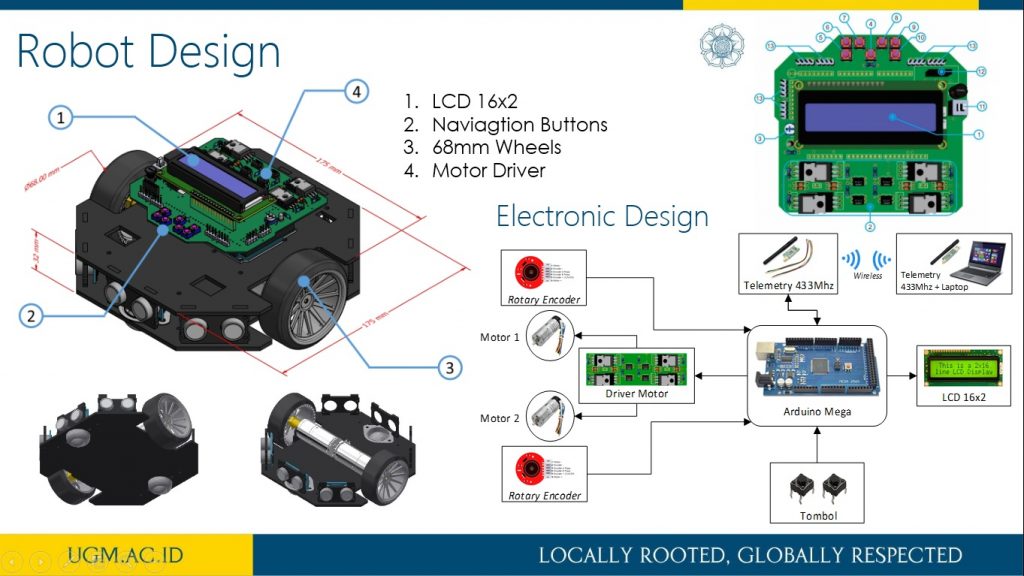
more detail visit our publication here.
Trajectory Tracking pada Robot Omni dengan Metode Odometry
Abstrak
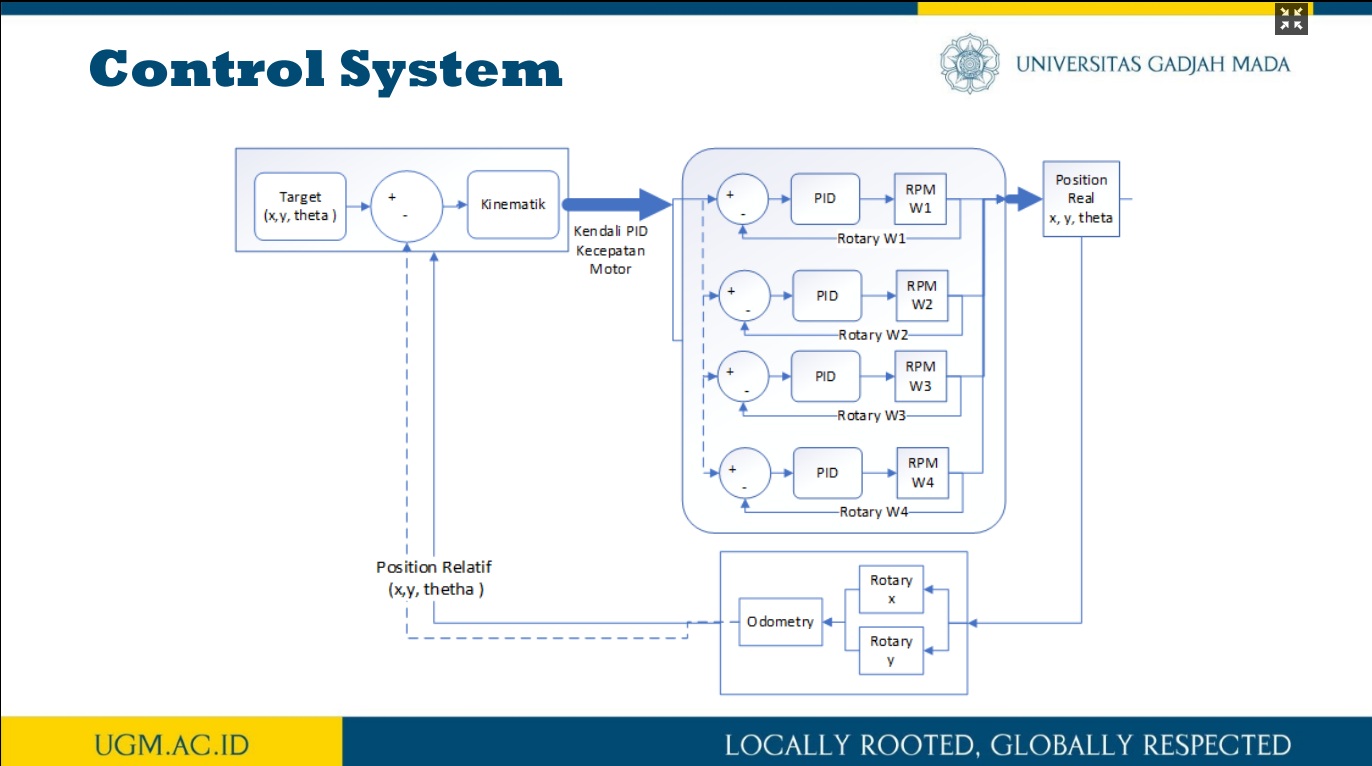
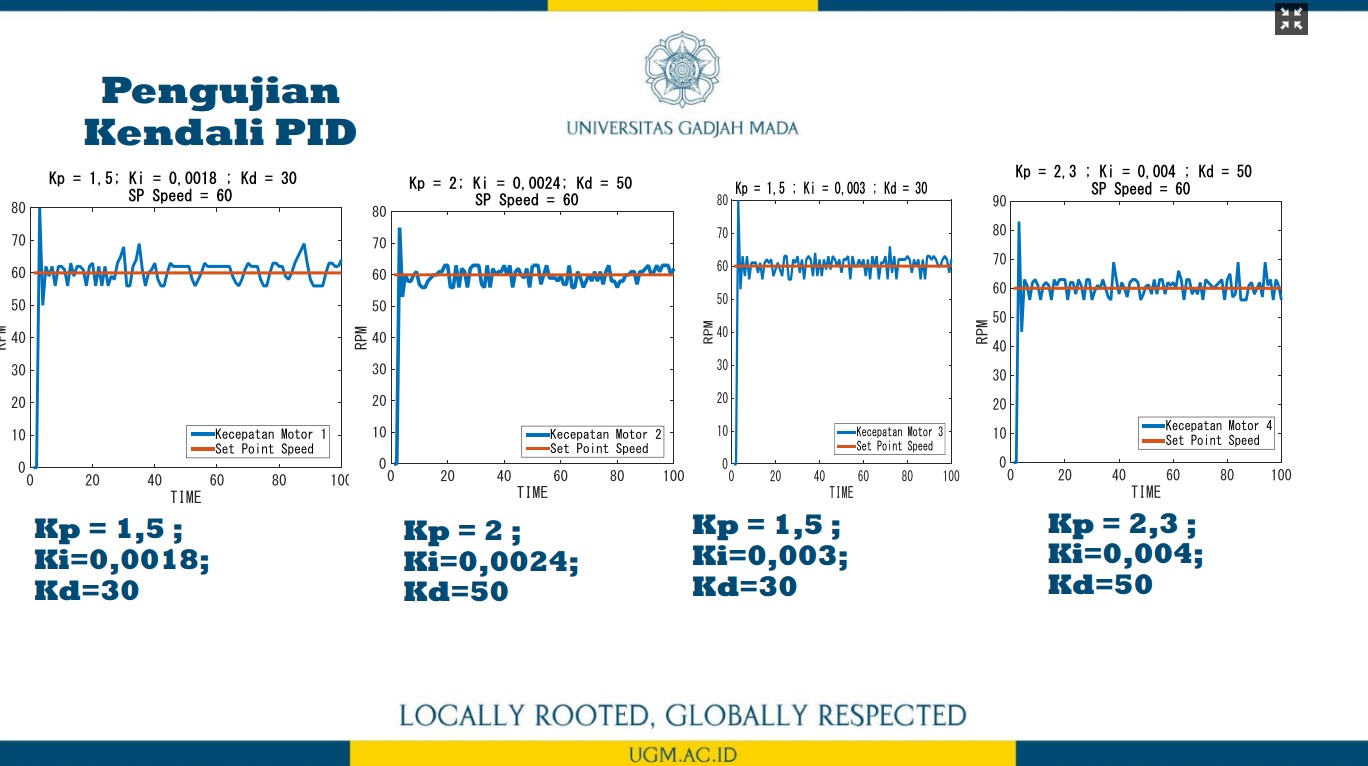
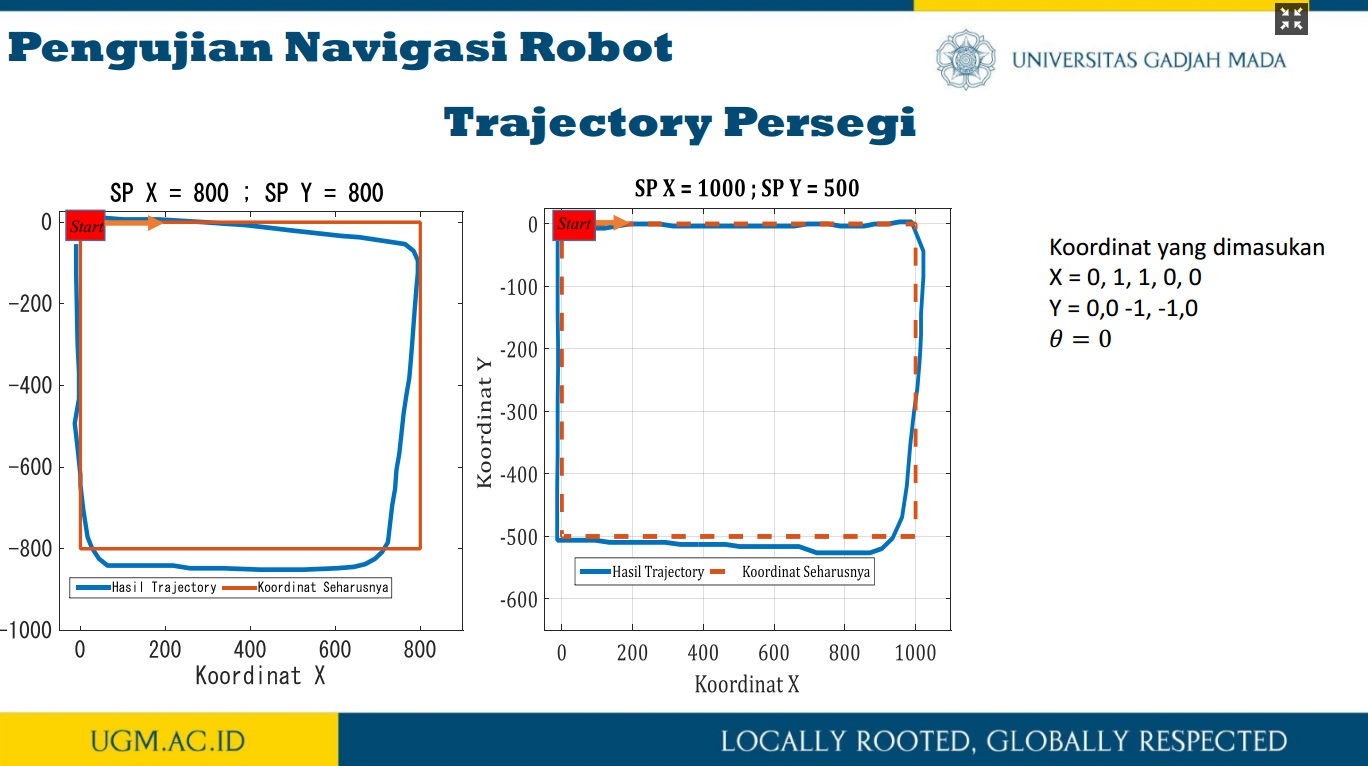
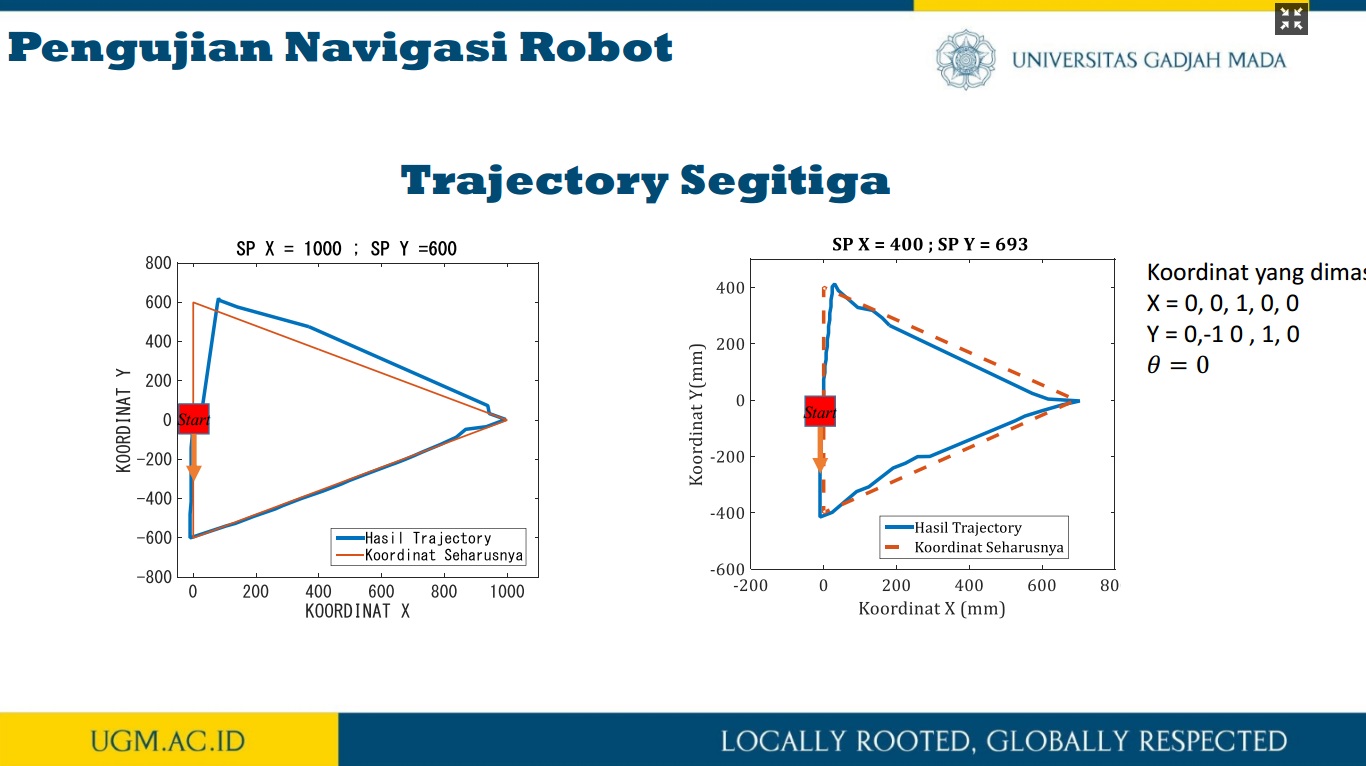
Penelitian ini memaparkan trajectory tracking pada robot omni dengan metode odometry. Sistem odometry bertujuan untuk memperkirakan posisi relatif terhadap posisi awal robot omni untuk memperkirakan perubahan posisi dari waktu ke waktu. Sensor rotary encoder digunakan untuk mencacah pergerakan robot omni pada koordinat x dan y pada proses perhitungan odometry. Selanjutnya, dengan menggunakan kinematika balik pada robot omni, nilai kecepatan putar masing-masing motor DC pada roda robot omni diperoleh. Selain itu, untuk memperoleh hasil pergerakan robot yang baik pada sistem odometry, kendali PID diterapkan untuk mengendalikan kecepatan putar masing-masing motor DC pada roda robot omni. Dengan kinematika balik dan sistem odometry, desain trajectory robot omni dapat dengan mudah dibangun. Untuk menguji kinerja metode odometry dalam melakukan proses trajectory tracking, terdapat tiga jenis pola pengujian trajectory, yaitu persegi panjang, segitiga sama sisi, dan segitiga sama kaki. Dari hasil pengujian ini, diperoleh nilai kesalahan di bawah 5%.
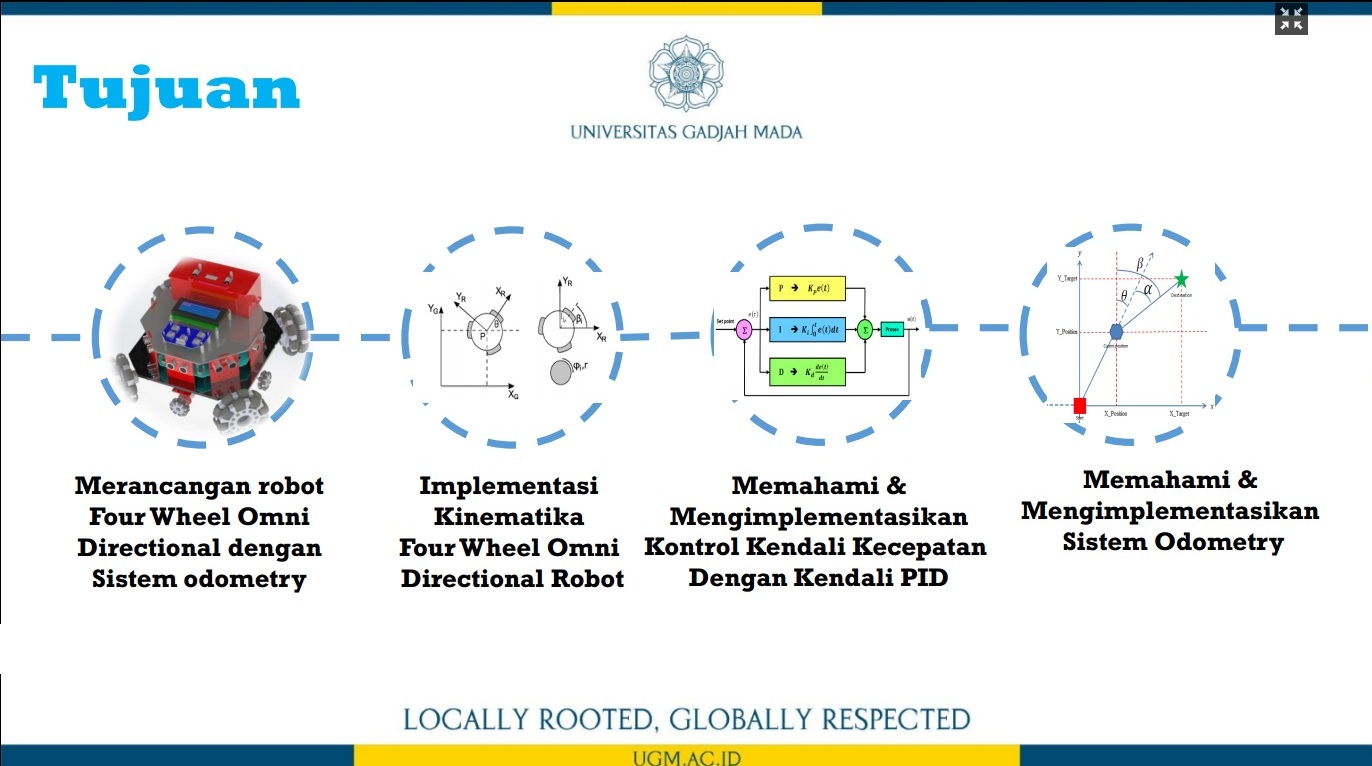
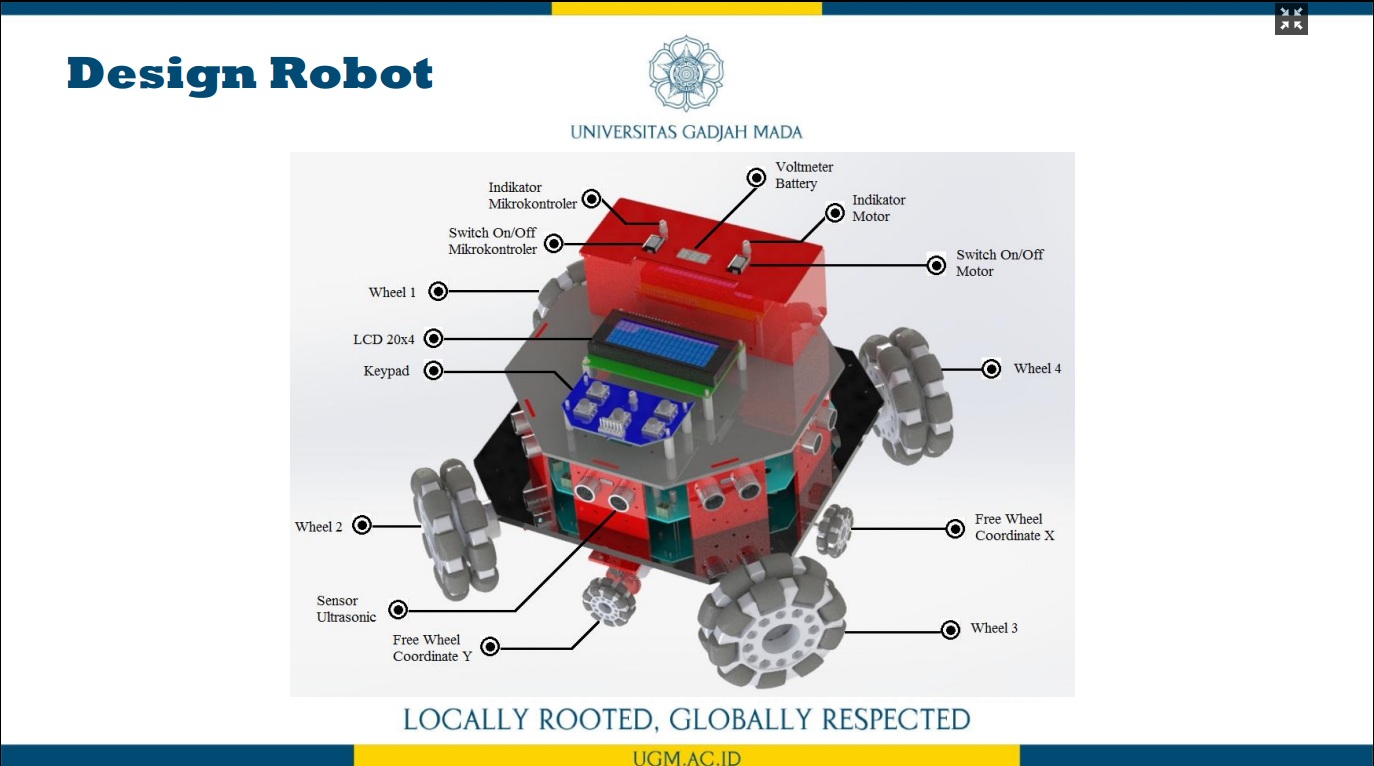

informasi lebih lanjut, silakan lihat publikasi kami di sini.
Autonomous Mobile Robot based on Behavior-Based Robotic using V-REP Simulator – Pioneer P3-DX Robot
Abstract
This research describes the design and implementation of behavior-based robotic (BBR) algorithm on a wheeled mobile robot (WMR) Pioneer P3-DX in a maze exploration mission using V-REP simulator. This robot must trace and search for targets placed randomly on a labyrinth. After successfully meeting the objective, robot runs back to home position using the nearest path. Robot navigation system applies BBR algorithm to reach the target using behavior modules which work simultaneously to obtain the desired robot’s trajectory. The most fundamental behavior which is highly affordable to build on the robot system is a wall-following behavior. To make the robot could follow the wall in a safe, smooth and responsive condition, proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller is applied. PID controller runs by utilizing the reading of sixteen proximity sensors carried on Pioneer P3-DX robot toward the expected wall distance while the robot is exploring the labyrinth. To ensure the designed system works properly, several tests were conducted, including BBR test and PID controller test. BBR test shows that the system can choose the shortest track when returning to home position. The PID controller test produces robot movement with maximum deviation and settling time for about 0.013 m and 30 seconds, respectively.

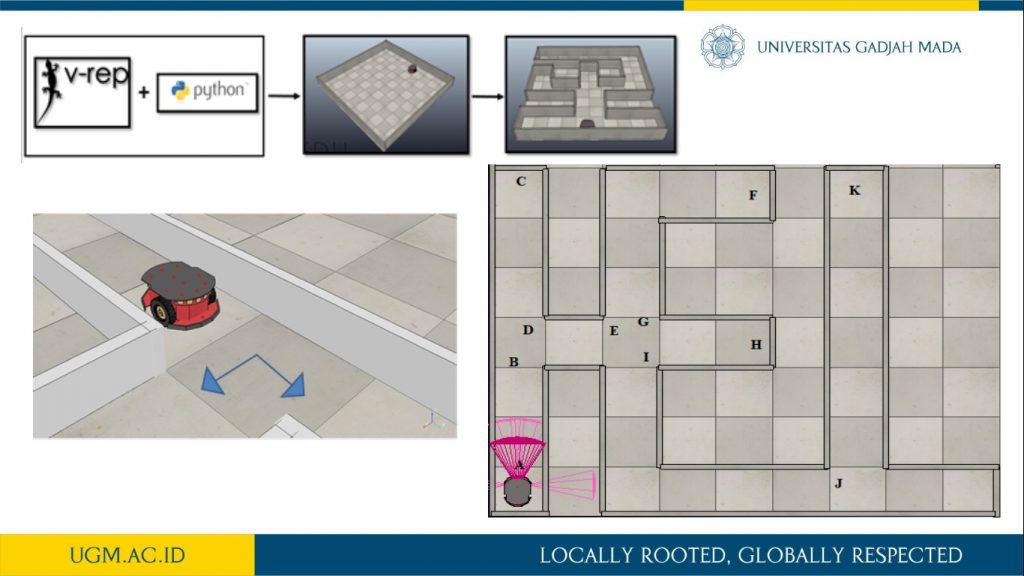
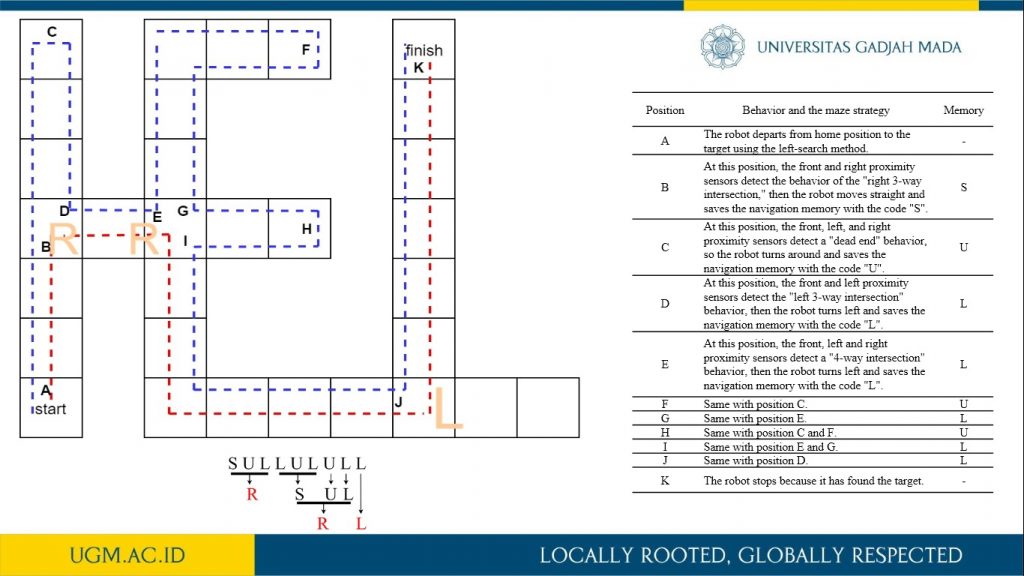
more detail visit our publication here.
Kendali Logika Fuzzy pada Car Like Mobile Robot (CLMR) Penjejak Garis
Abstrak
Penelitian ini memaparkan perancangan sistem kendali logika fuzzy untuk mengatur kecepatan dan arah sudut steering pada car like mobile robot (CLMR) dengan menggunakan metode Ackermann steering. CLMR penjejak garis dirancang menggunakan 16 buah photodiode, dan terdapat 7 buah membership fuzzfikasi dari pembacaan error dan last error sehingga terbentuk 49 aturan. Untuk menguji perfoma kendali fuzzy pada sistem CLMR dalam mengikuti lintasan garis maka dilakukan pengujian dengan bentuk lintasan berupa garis lurus dan berbelok serta zig-zag dalam satu lintasan putar. Proses variasi nilai keanggotaan fuzzifikasi masukan dan defuzzifikasi keluaran dilakukan sebanyak lima kali. Dari hasil pengujian diperoleh bahwa kendali logika fuzzy yang diaplikasikan pada sistem mampu membuat pergerakan CLMR sukses mengikuti lintasan uji selama 9,38 detik lebih baik 0,53 detik dari kendali PID. Selanjutnya, hasil rancangan sistem CLMR ini merupakan sebuah prototipe self-driving car.
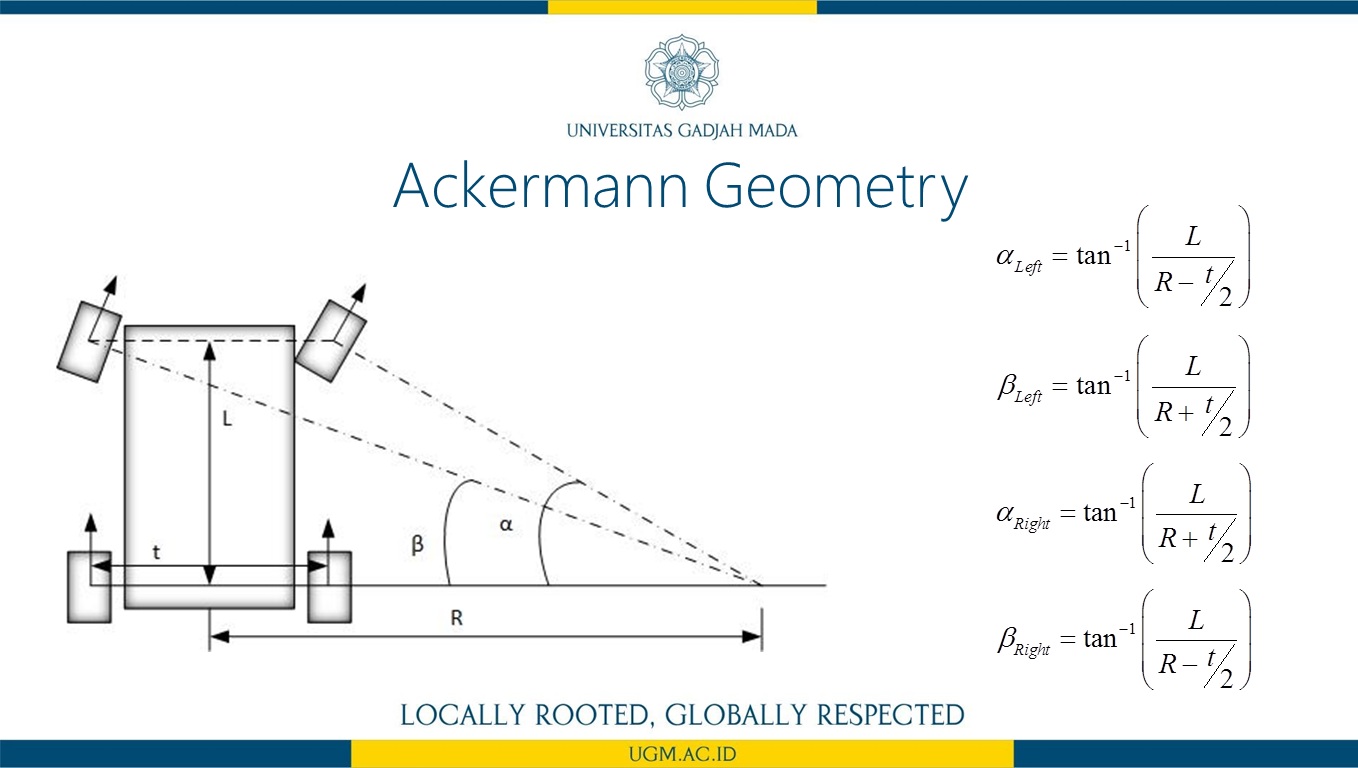
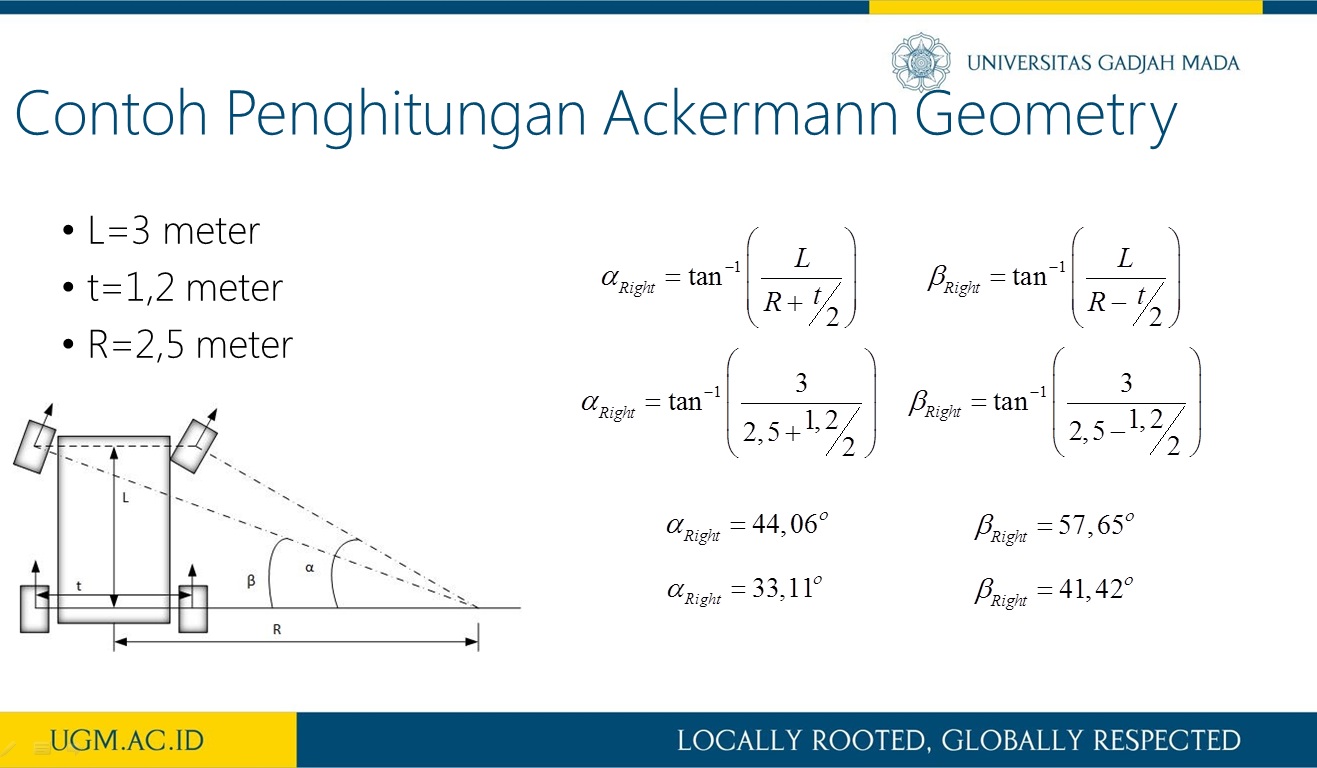
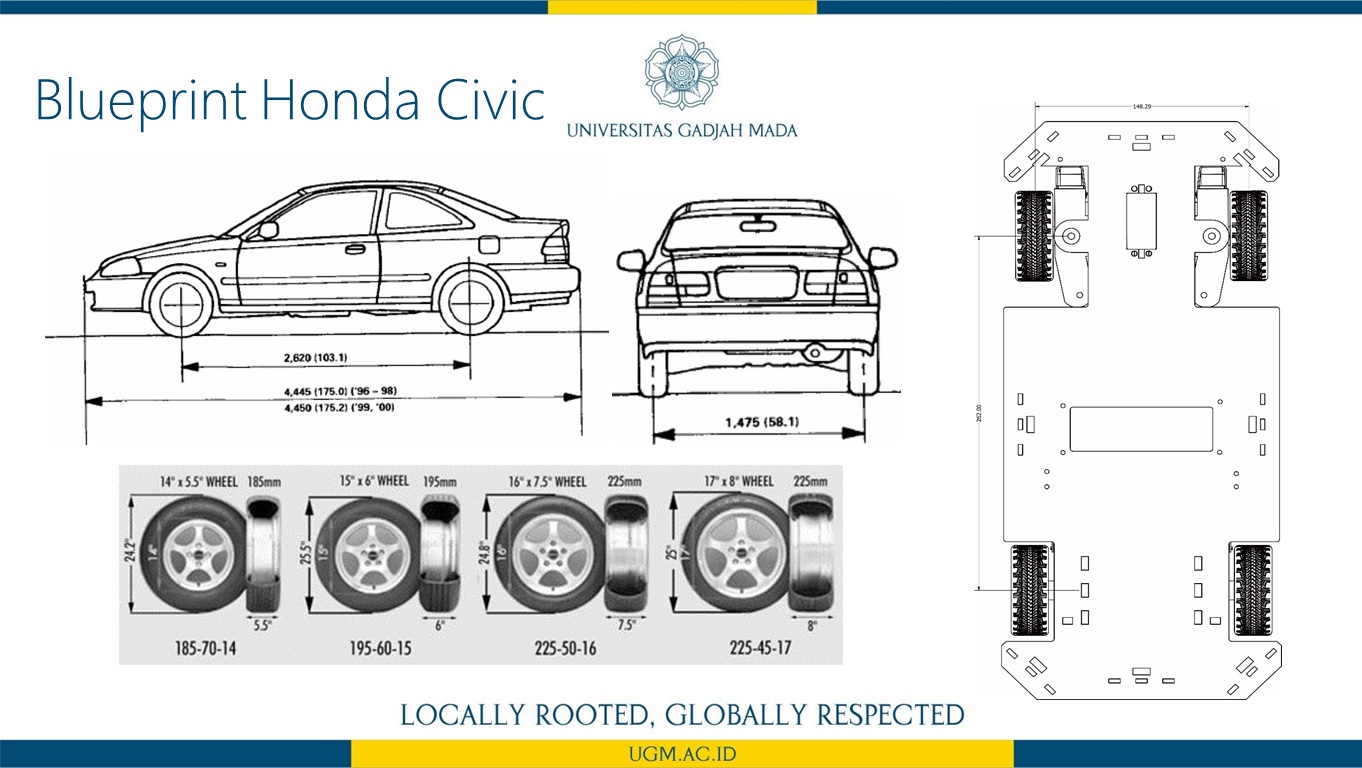


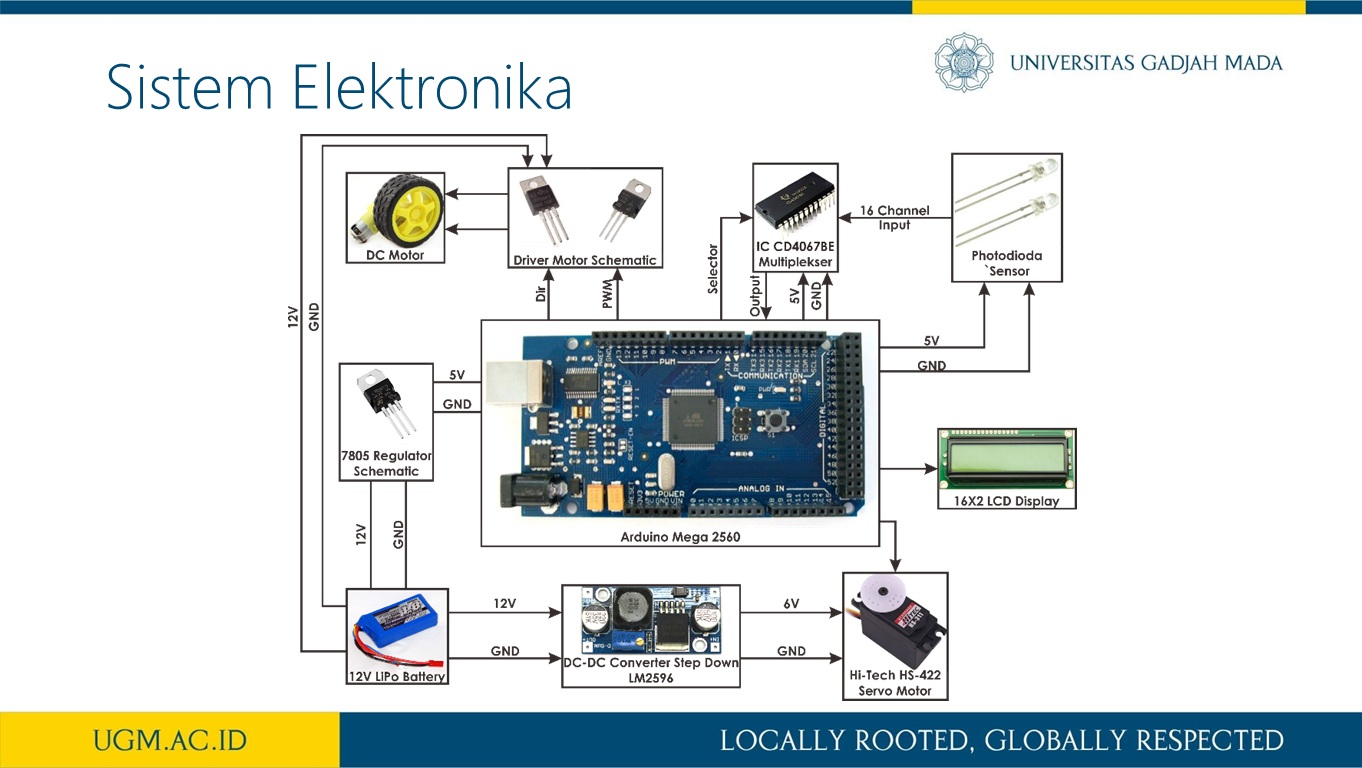

informasi lebih lanjut, silakan lihat publikasi kami di sini.
Robot Inverted Pendulum Beroda Dua (IPBD) dengan Kendali Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
Abstrak
Penelitian ini memaparkan proses pemodelan robot inverted pendulum beroda dua (IPBD) menggunakan dinamika Lagrange. Setelah sistem model robot IPBD diperoleh, teknik kendali optimal dalam hal ini menggunakan linear quadratic regulator (LQR) digunakan untuk melihat step respon sistem dan tanggapan respon sistem terhadap gangguan. Sebelum kendali LQR diimplementasikan, simulasi menggunakan Simulink Matlab dilakukan untuk mendapat parameter gain K pada kendali LQR. Selanjutnya, dengan mengubah-ubah matriks pembobot Q akan diperoleh variasi gain K. Pada penelitian ini dilakukan variasi matriks pembobotan Q sebanyak lima jenis. Sedangkan matriks elemen R di-tuning dengan nilai satu. Dari hasil pengujian diperoleh bahwa dengan membesarkan pembobotan matriks Q, dihasilkan respon menuju keadaan steady lebih cepat dan overshoot berkurang. Parameter gain K dari hasil simulasi selanjutnya akan diimplementasikan secara embedded programming ke dalam Arduino Uno pada sistem robot IPBD.
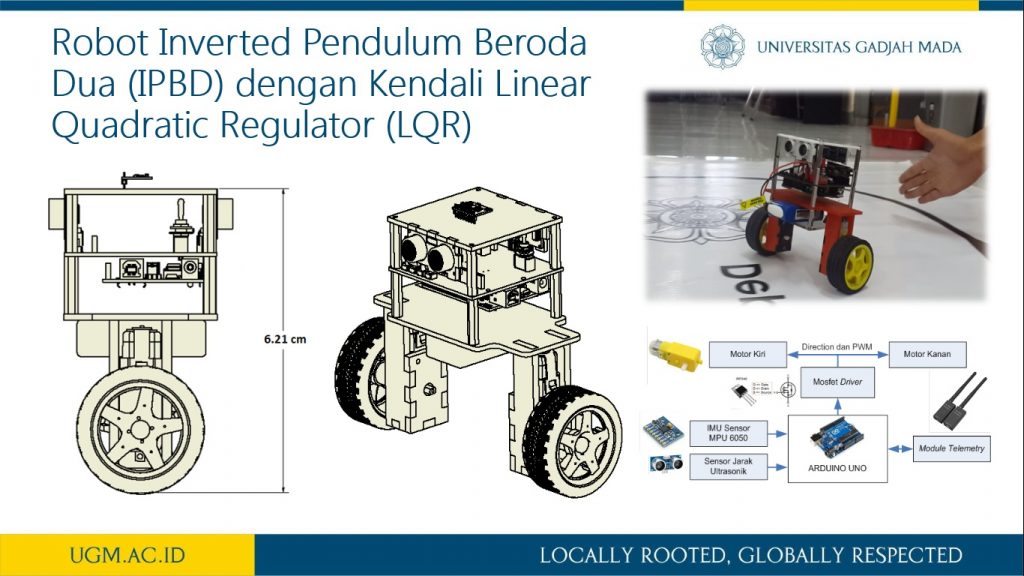
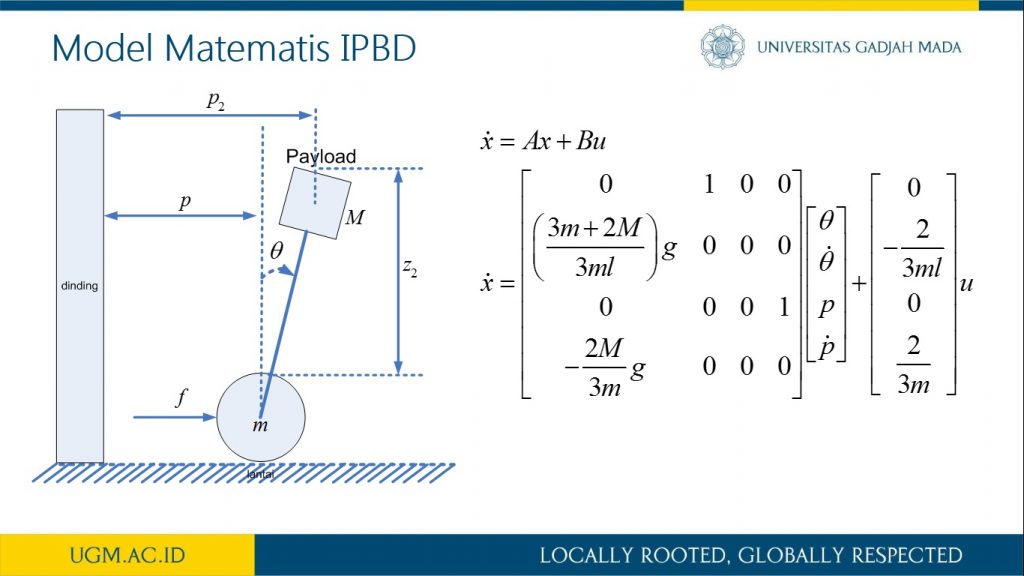
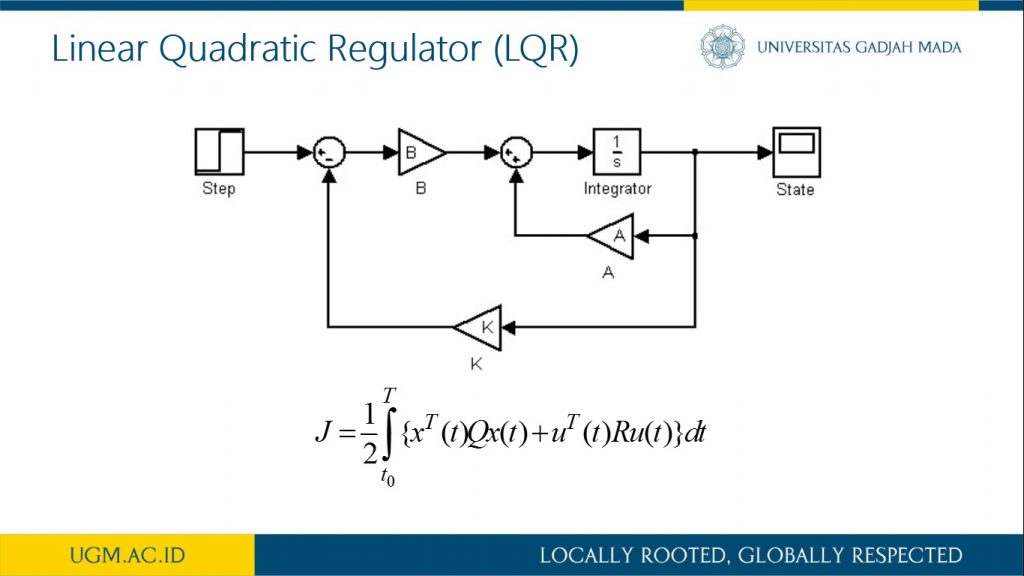
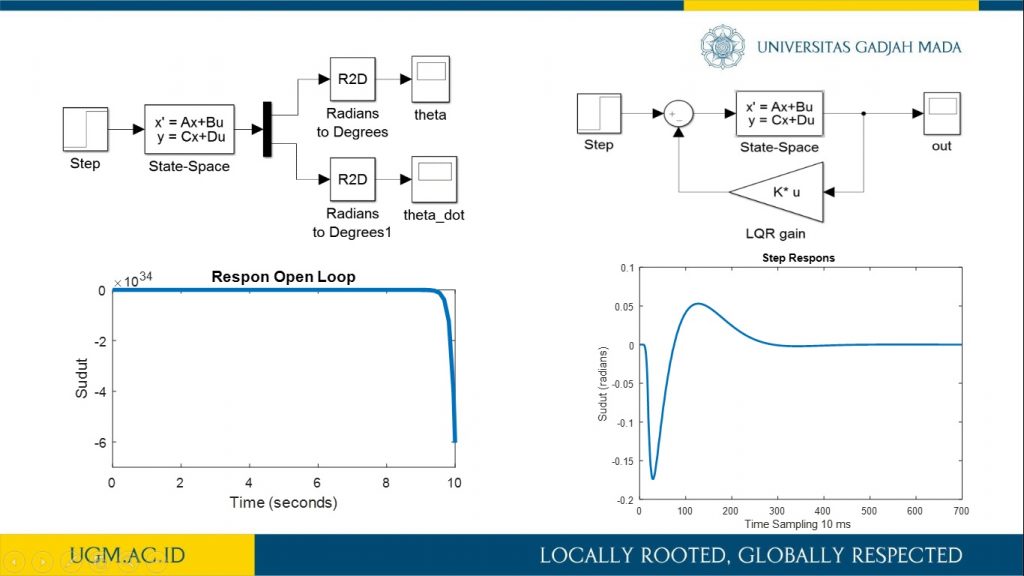
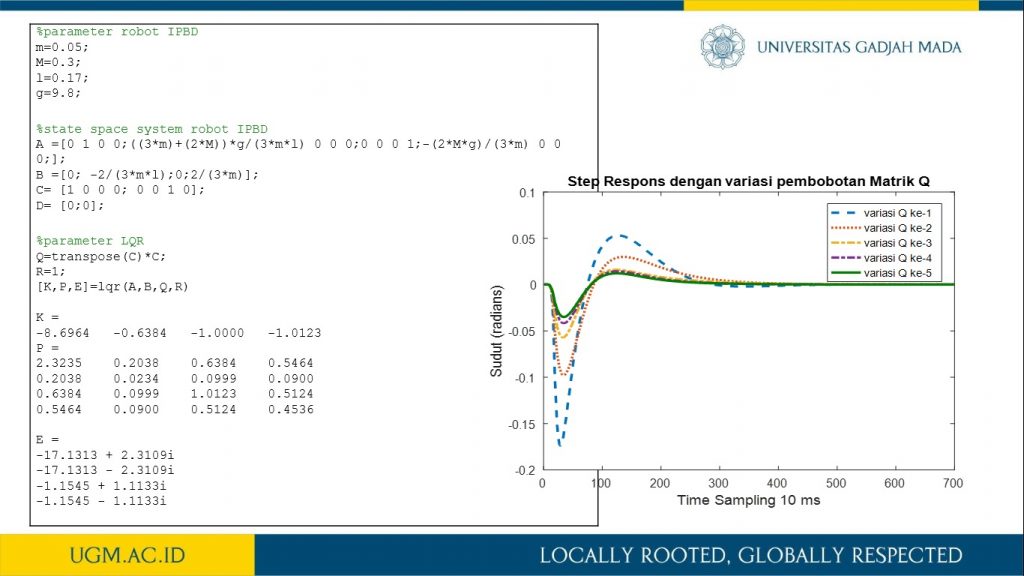
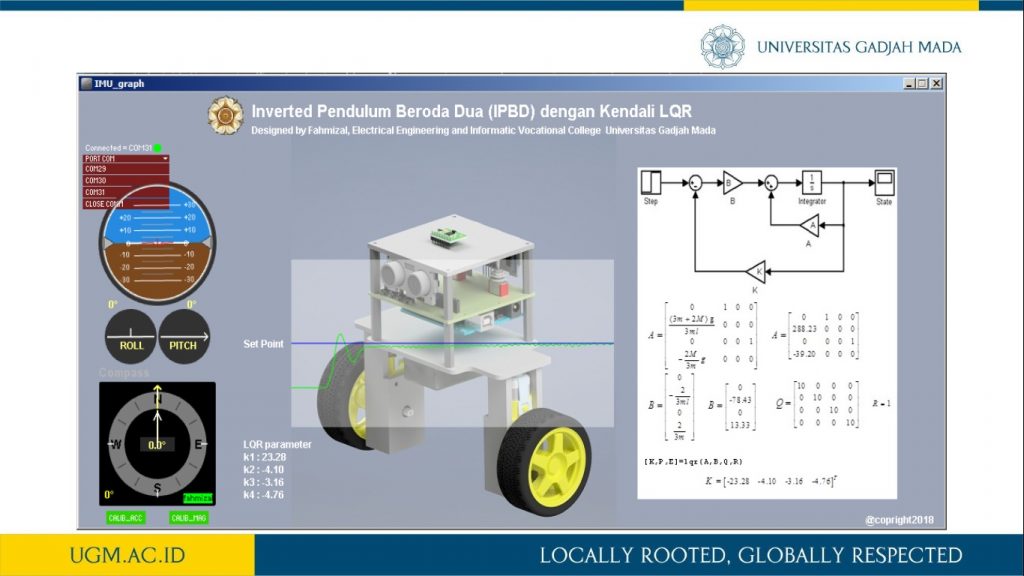
informasi lebih lanjut, silakan lihat publikasi kami di sini.
Logika Fuzzy pada Robot Inverted Pendulum Beroda Dua (IPBD)
Abstrak
Robot inverted pendulum beroda dua (IPBD) merupakan sistem yang tidak stabil dan bersifat non-linear. Motor DC sebagai penggerak robot yang terletak pada masing-masing roda kiri dan kanan memberikan variabel gaya untuk mempertahankan kestabilan robot. Oleh karena itu diperlukan suatu kendali yang dapat menjaga keseimbangan dari robot. Makalah ini memaparkan kendali logika fuzzy dalam hal pengendali keseimbangan robot. Pada perancangan robot ini, penulis menggunakan senor inertia measurement unit (IMU) versi MPU 6050 sebagai sensor pendeteksi keseimbangan robot. Nilai setpoint sudut robot yang diberikan adalah sudut elevasi robot terhadap sumbu horizontal atau pada sumbu pitch. Selanjutnya, nilai keluaran sensor IMU dibandingkan dengan setpoint. Lebih lanjut, nilai kesalahan (error) dan nilai perubahan kesalahan (delta errror) yang dihasilkan akan digunakan sebagai masukan logika fuzzy. Hubungan relasi masukan fuzzy diselesaikan dengan aturan Mamdani. Keluaran dari logika fuzzy diselesaikan dengan perhitungan weight average (WA). Hasil keluaran logika fuzzy berupa nilai putaran motor kiri dan kanan yang dikendalikan dengan cara mengatur lebar pulsa sinyal pulse with modulation (PWM). Dari hasil pengujian diperoleh bahwa kendali logika fuzzy yang diaplikasikan pada robot IPBD dapat menjaga keseimbangan robot dengan osilasi pada sudut -2 hingga 2 derajat.
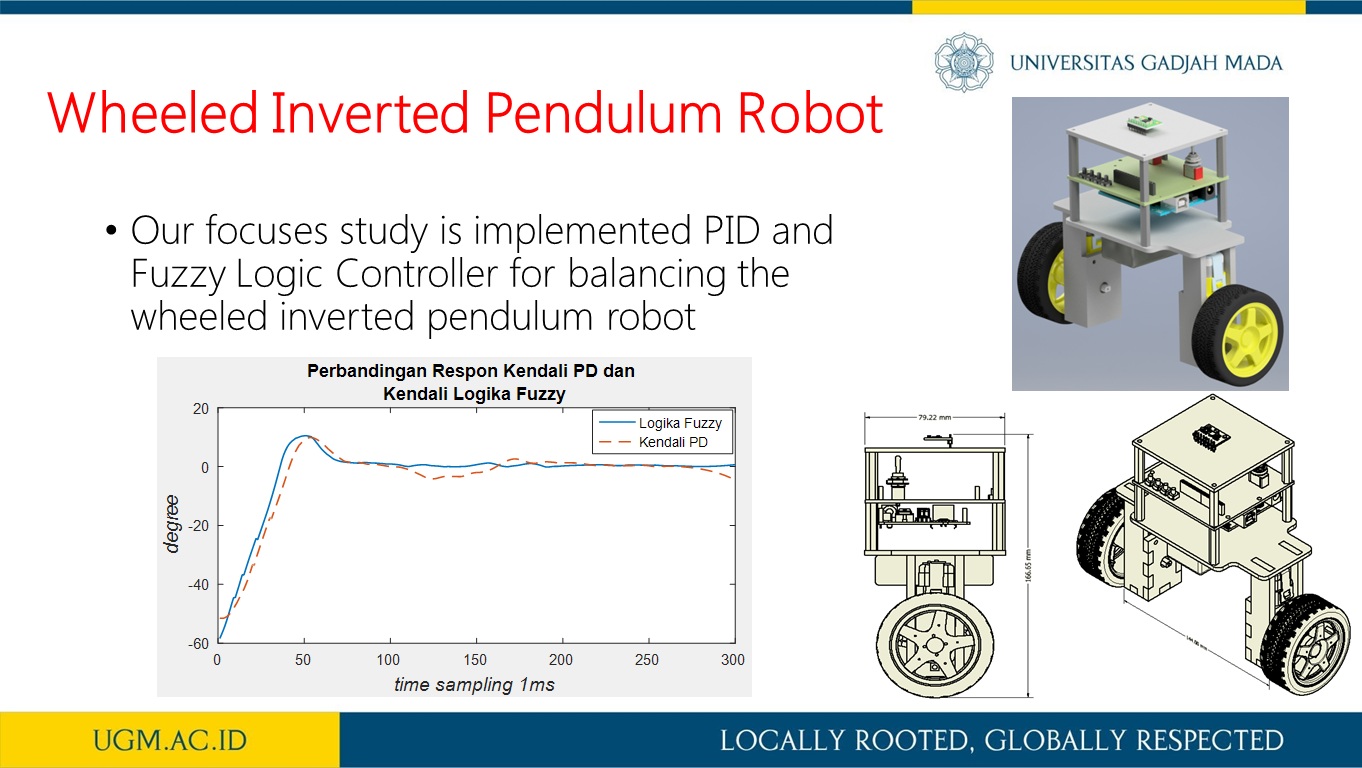
informasi lebih lanjut, silakan lihat publikasi kami di sini.
Trajectory and Heading Tracking of a Mecanum Wheeled Robot using Fuzzy Logic Control
Abstract
This research presents trajectory tracking and heading adjustment systems of a Mecanum wheel robot using fuzzy logic controller (FLC) and inertia measurement unit (IMU) sensor. It is known that when a Mecanum wheel robot moves, its wheels may slip due to various floor conditions. During such a slip condition, the exact position and orientation of the robot often deviate from that which was intended. In order to reduce the size of this deviation, the Mecanum wheel was equipped with an IMU sensor which measures the orientation (heading) of the Mecanum wheel robot. The implementation of the IMU sensor as a heading sensor usually achieved using a complementary filterThe FLC, on the other hand, is used to force the Mecanum wheel robot to follow a given trajectory with minimum heading deviation. As a result, the FLC system and the IMU sensor provide a robust navigation scheme for Mecanum wheel robot without the need for external references such as beacons or visual markers. The implementation of our approach on the Mecanum wheel robot was achieved using embedded microcontroller for motion control and information acquisition. The developed FLC system was also deployed with a friendly graphical user interface which allows for the adjustment of fuzzification methods.
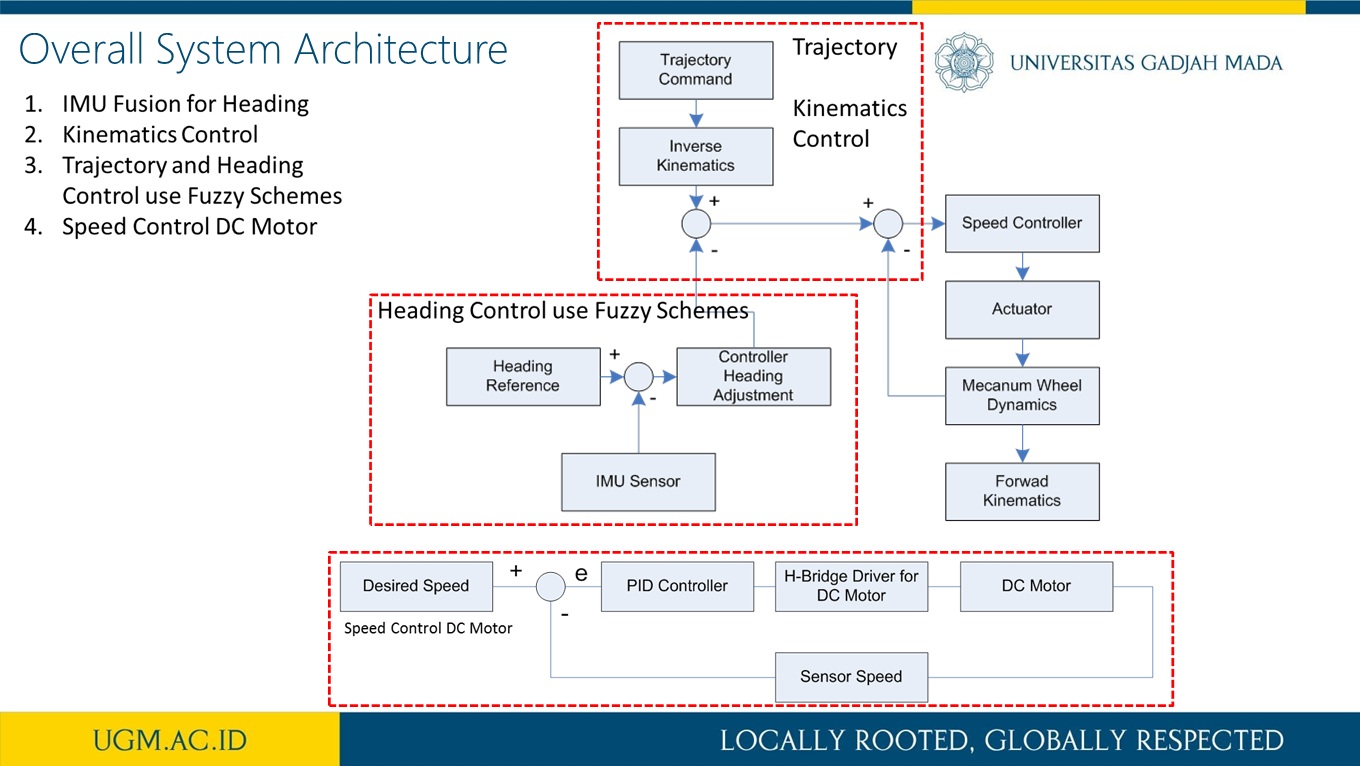
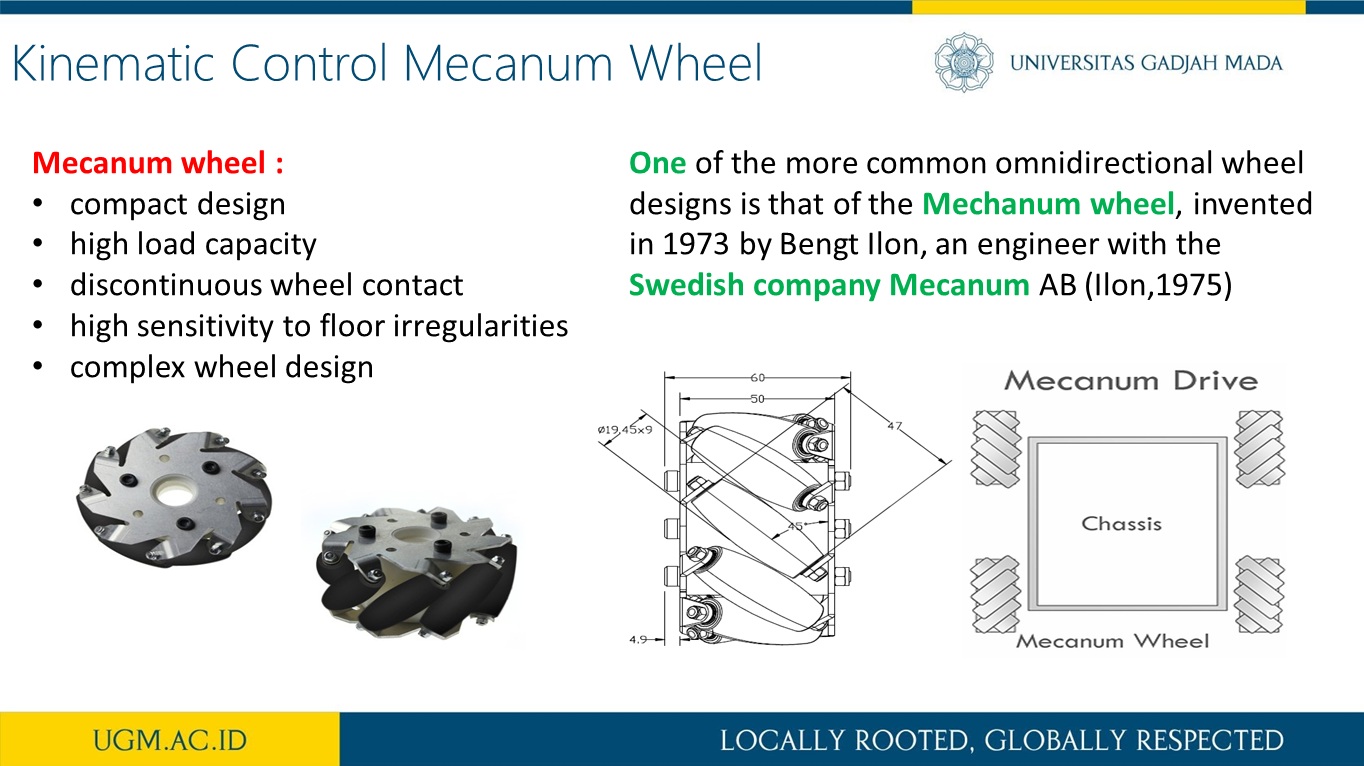
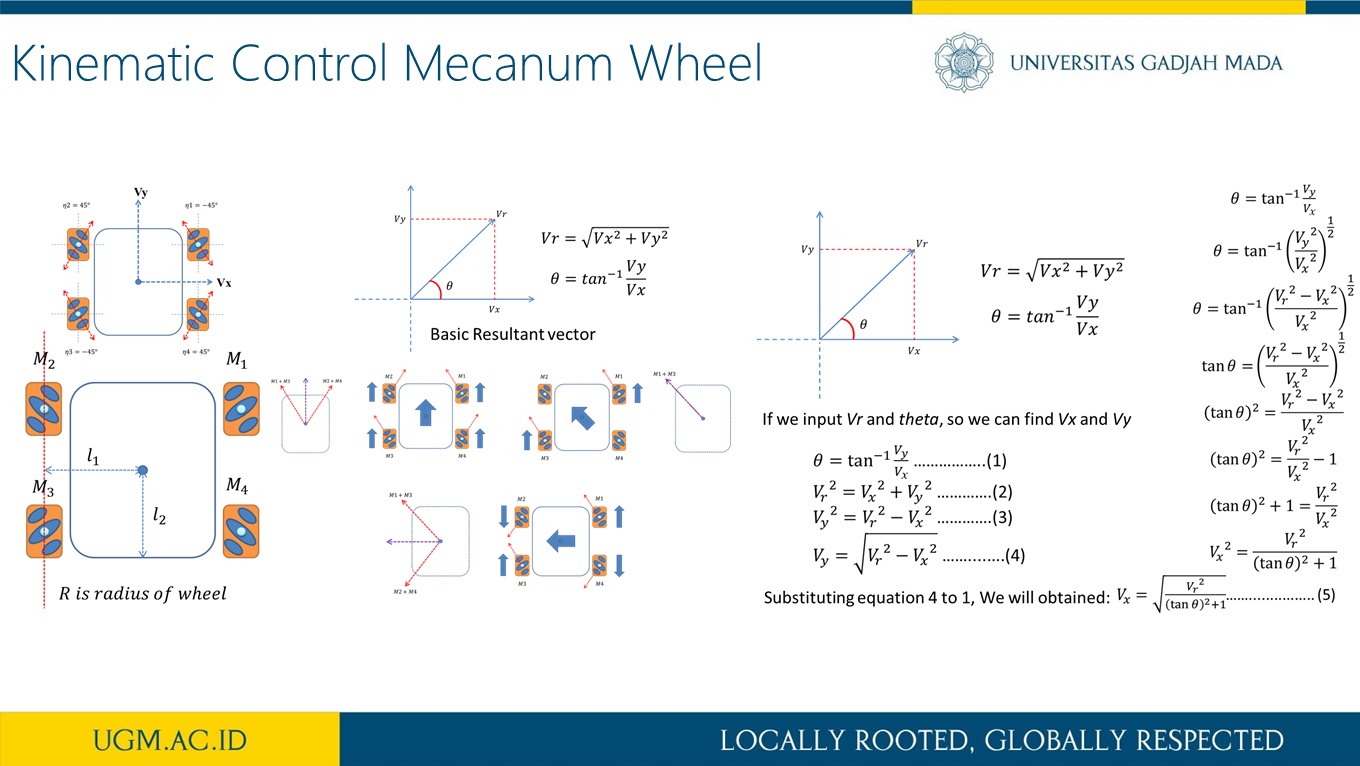
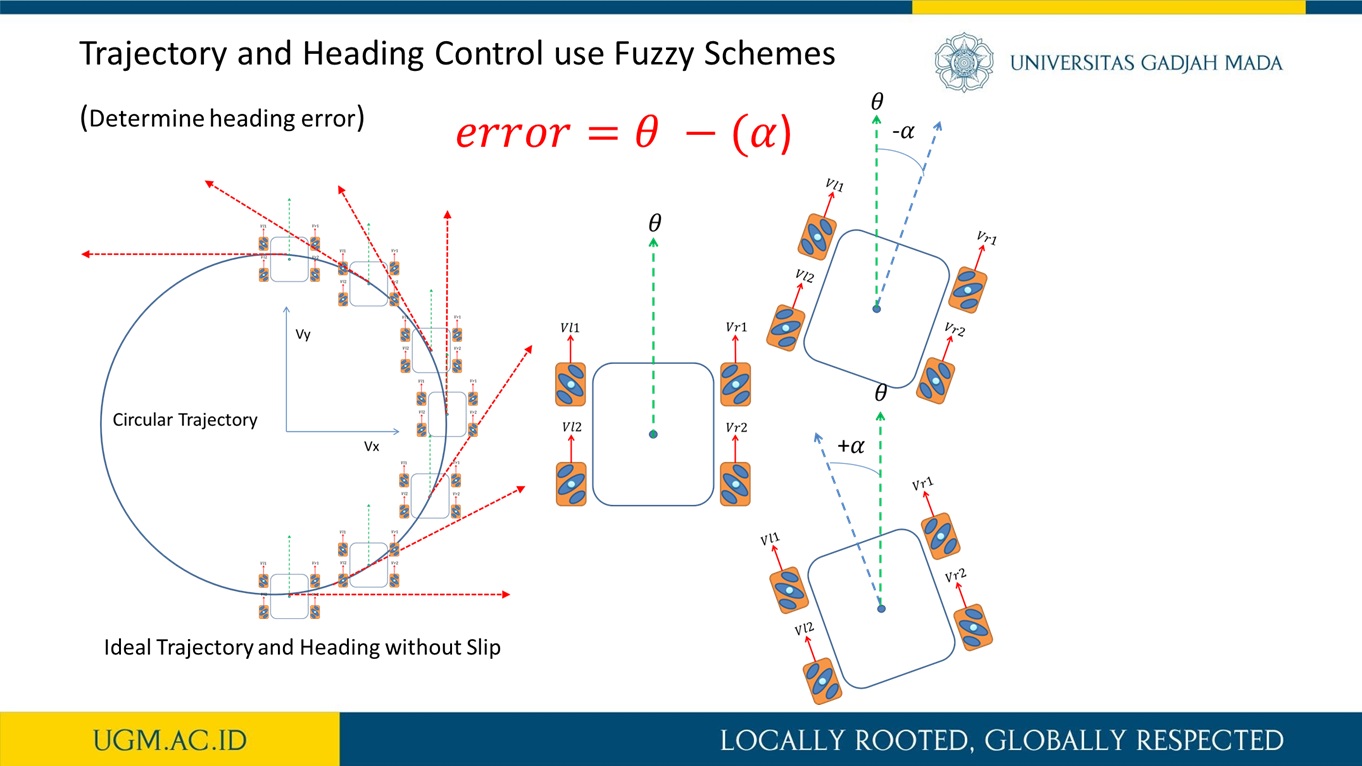

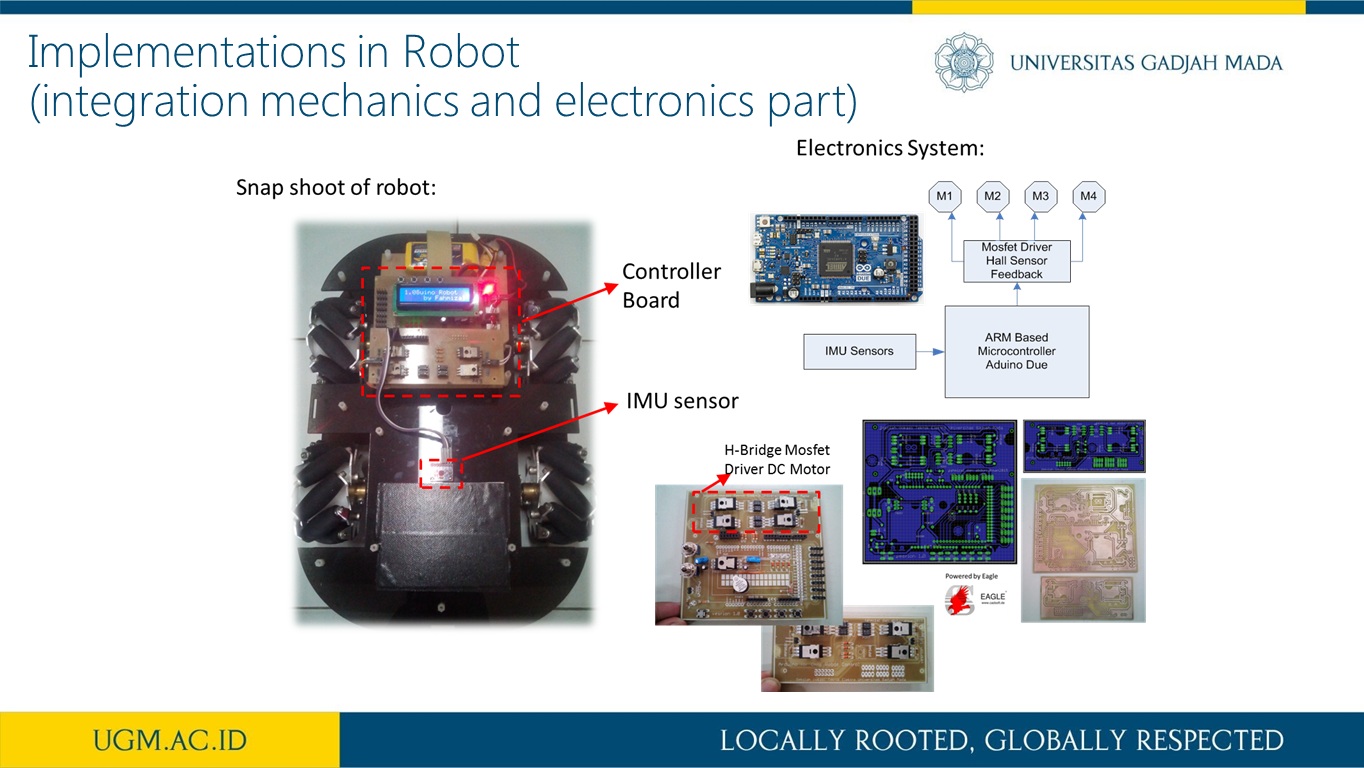
more detail visit our publication here
Recent Comments